The Top 6 Sustainable Architecture Strategies for Public Building Design
More and more, sustainable building design is becoming a key part of how public buildings are planned and built. While cost is always an important factor for civic planners, investing in sustainable strategies from the start can save money over time. Beyond financial benefits, these designs improve air quality, promote well-being, and support a healthier, more sustainable future.
What is Sustainable Building Design?
Sustainable building design is the practice of creating buildings that minimize negative impacts on the environment. Architects focus on using the natural features of a site, managing energy efficiently, and handling stormwater responsibly. They also choose environmentally friendly materials and systems to reduce the building’s overall footprint.
Sustainable building design is no longer a trend for the future—it’s a critical need today. Communities that embrace these practices can enjoy long-term economic, social, and environmental benefits.
Top Sustainable Architecture Strategies
When designing public buildings with sustainability in mind, architects often use a combination of strategies to make the building efficient, healthy, and environmentally responsible. Here are the key strategies:
1. Passive Sustainable Design
Passive strategies reduce energy use by working with the natural environment. This includes:
- Orienting the building to take advantage of the sun and prevailing winds.
- Placing windows strategically to improve natural lighting and ventilation.
- Using thermal mass, such as thick walls, to absorb heat during the day and release it at night, keeping the building comfortable without heavy energy use.
2. Active Sustainable Design
Active strategies involve mechanical systems designed for efficiency. Architects work with engineers to implement:
- High-efficiency HVAC (heating, ventilation, and air conditioning) systems
- Energy-efficient lighting and
- Advanced electrical systems
These systems reduce energy and water use while lowering the building’s environmental footprint.
3. Renewable Energy Systems
Using renewable energy is a major part of sustainable building design. Solar panels, wind turbines, or other renewable technologies can provide clean energy for the building. Often, these systems are combined with passive strategies to maximize energy efficiency.
4. Green Building Materials
Materials matter in sustainable building design. Choosing recycled or responsibly sourced steel, lumber, concrete, and finishing materials like carpets and furniture reduces environmental impact. These choices support eco-friendly manufacturing and lower the carbon footprint of the building.
5. Native Landscaping
Landscaping plays a vital role in water conservation and energy efficiency. Using native trees, plants, and grasses reduces irrigation needs and helps the building blend naturally with its environment. Strategically placed trees can also shade the building, lowering cooling costs.
6. Stormwater Management
Buildings and paved areas prevent water from naturally soaking into the ground, leading to runoff and potential flooding. Sustainable building design includes stormwater management strategies like:
- Pervious pavements that allow water to filter through
- Retention ponds that capture and slowly release water
- Bioswales that filter and manage stormwater efficiently
These measures help protect natural water systems and prevent environmental damage.
Examples of Sustainable Building Design in Practice
At HMC Architects, sustainable building design is applied to every public project. These projects not only reduce environmental impact but also serve as learning tools for the community. Here are some examples:
Quail Hill Community Center
Located in Irvine, California, Quail Hill Community Center is designed to exist in harmony with nature. The building uses solar panels and energy-efficient LED lighting to reduce energy consumption. Low-flow water fixtures save water, while native landscaping reduces irrigation needs. Informational signage educates visitors about sustainability, making the center both functional and educational.
The Frontier Project
In Rancho Cucamonga, California, the Frontier Project serves as an educational model for sustainability. Key sustainable building design features include:
- Sloped walls that allow more natural light inside
- Views of native trees and plants to connect occupants with nature
- A cooling tower that uses water evaporation to naturally cool the building
- Thermal mass walls to regulate interior temperature
- Stormwater management using a bioswale to capture and reuse water
The Frontier Project achieved LEED Platinum certification, making it one of the most sustainable facilities in California.
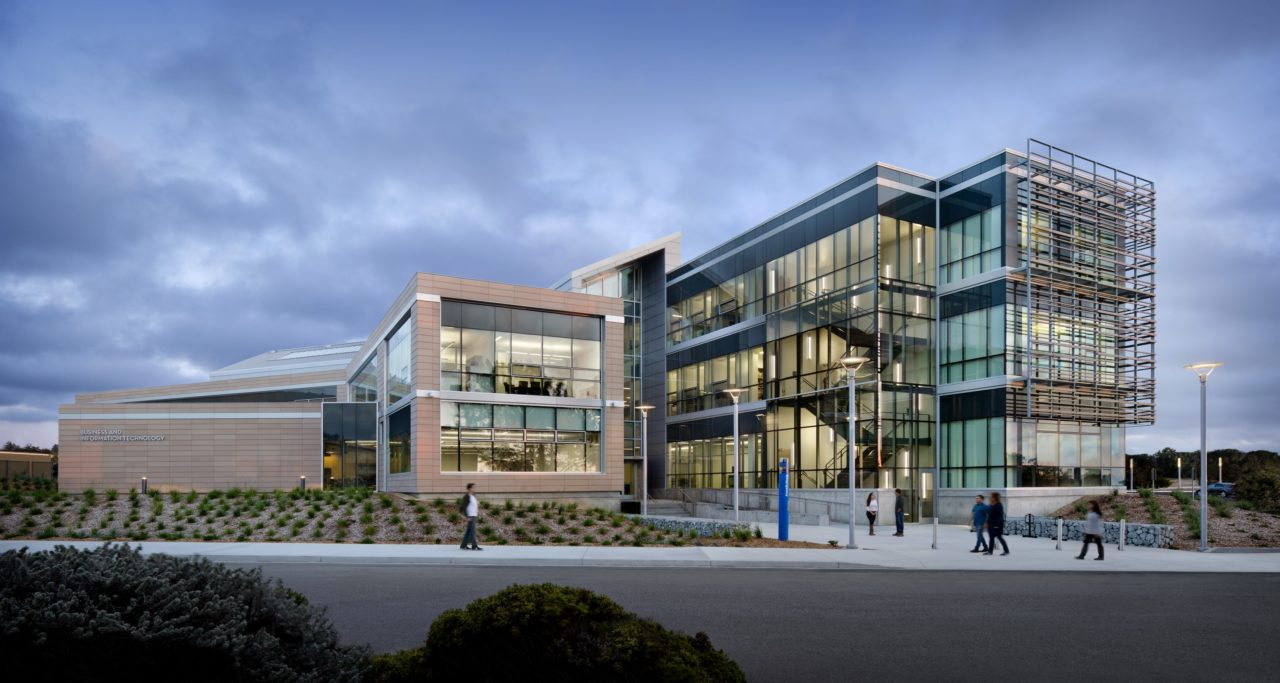
CSU Monterey Bay Joel and Dena Gambord Building
This business and IT building is designed to achieve LEED Gold certification. It features:
- An atrium and glass walls to maximize daylight
- Water and energy-saving strategies
- A double-skin wall system and exterior screens to control heat gain
These elements make the building efficient, comfortable, and environmentally responsible.
Achieving Sustainable Building Design
Designing a sustainable public building does not have to be complicated. Experienced architects can provide solutions that fit your goals and budget while maximizing environmental benefits.
At HMC Architects, sustainable building design is central to every project. By combining innovative strategies with practical solutions, we create buildings that serve communities, protect the environment, and educate the public. If you want to learn more about how sustainable strategies can be applied to your civic project, contact HMC Architects today.